Python Dictionary | What is Dictionary in Python?
(Best 5 Minute Revision)
When learning Python, one of the most essential and versatile data collection type you will come through is the Python Dictionary. This blog will help you understand what a dictionary in Python is, how it works, and why it’s such a powerful tool for programmers.
So, let’s begin…!!
Introduction
A dictionary in Python is an unordered, mutable collection of key-value pairs. Each key must be unique, and it maps to a corresponding value. Unlike lists and tuples that store values using numeric indices, dictionaries use keys to store and retrieve data. This makes data lookup faster and more intuitive, especially when the keys are meaningful, such as names, IDs, or labels.
Dictionaries are the ideal choice when you want to establish or visualize the relationship between data. For example, storing student names and their grades, product names and their prices, or countries and their capitals. Python dictionaries allow you to represent these relationships between data clearly and access values quickly using descriptive keys.
Characteristics of Python Dictionary
Unordered: Items do not have a defined order (until Python 3.7, where insertion order is preserved).
Mutable: You can add, change, or delete key-value pairs.
Indexed by Keys: Instead of numeric indexes, dictionaries use keys to access their values.
No Duplicate Keys: Each key must be unique. If a key is repeated, the last value overwrites the previous one.
Working with Dictionary
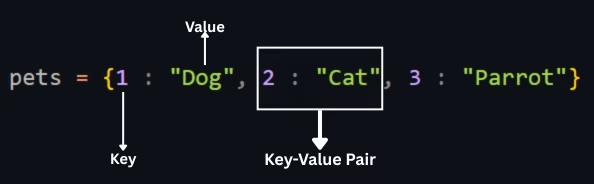
Dictionary is usually declared using curly braces {} or dict() constructor. This how we declare dictionary:
pets = {1 : “Dog”, 2 : “Cat”, 3 : “Parrot”}
or
pets = dict(1 = “Dog“, 2 = “Cat“, 3 = “Parrot”)
Here, 1, 2, and 3 are keys whereas “Dog”, “Cat”, and “Parrot” are the values stored with reference to these keys, respectively.
Useful Dictionary Methods
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
.get(key) | Returns the value or None if not found |
.keys() | Returns all keys in the dictionary |
.values() | Returns all values |
.items() | Returns all key-value pairs as tuples |
.pop(key) | Removes the specified key |
Nested Dictionary
A nested dictionary is a dictionary where the values themselves are dictionaries. This allows for hierarchical data representation, which is especially useful in real-world scenarios like storing student records, employee data, or configuration options.
For example, we need to save data of students in a class:
students_age = {
‘student1’: {‘name’: ‘Alice’, ‘age’: 12},
‘student2’: {‘name’: ‘Bob’, ‘age’: 15},
‘student3’: {‘name’: ‘Charlie’, ‘age’: 18}
}
You can access the data like this:
students_age[‘student2’][‘age’] # Output: 15
Nested dictionaries are useful when each key represents a unique entity and you want to associate multiple attributes with it.
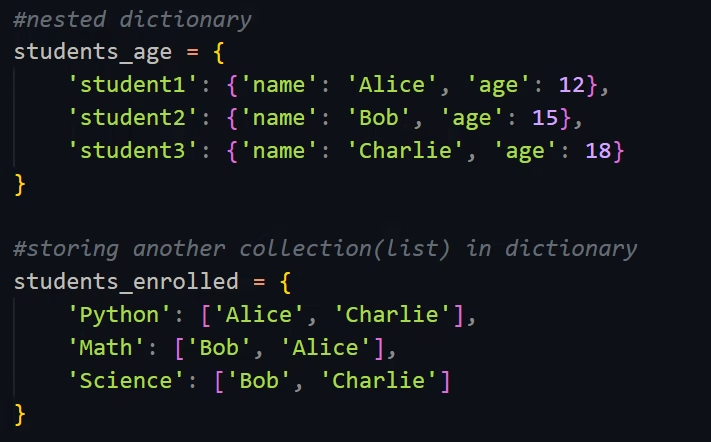
Storing Collections in Dictionary
A dictionary in Python can also store other data collections, such as lists, sets, or dictionaries, as its values. This is helpful when one key maps to multiple values.
For example,
students_enrolled = {
‘Python’: [‘Alice’, ‘Charlie’],
‘Math’: [‘Bob’, ‘Alice’],
‘Science’: [‘Bob’, ‘Charlie’]
}
Here, the value for each subject is a list of students enrolled in it. This structure is ideal for handling categorized or grouped data.
Benefits of Using Python Dictionary
Efficient lookups for large datasets.
Easily readable and maintainable structure.
Flexible for storing complex data relationships.
Ideal for tasks involving mapping, categorizing, or grouping data.
FAQs About Python Dictionary
Q1. Can dictionary keys be duplicated?
No, dictionary keys must be unique.
Q2. Can values be duplicated in a dictionary?
Yes, values can be duplicated even if the keys are unique.
Q3. Is dictionary mutable in Python?
Yes, dictionaries are mutable — you can add, modify, or remove items.
Q4. What data types can be used as dictionary keys?
Only immutable data types like strings, numbers, or tuples can be used as keys.
Q5. What is the default return value of get() if the key is not found?
The get() method returns None if the key is not found.
Conclusion
A Python Dictionary is one of the most useful tools in your coding arsenal. Whether you’re building a simple project or working on advanced data-driven applications, understanding how to effectively use dictionaries will significantly improve your coding efficiency.
In essence, a dictionary in Python lets you organize data in a logical and readable format, making your programs easier to build and debug. With support for nesting and storing collections, dictionaries are incredibly versatile and scalable.
If you’re serious about learning Python, make sure to visit and explore our Python for Beginners article — it includes exercises, examples, and a complete roadmap to mastering Python, step by step.
See you in the next blog, till then keep learning!!